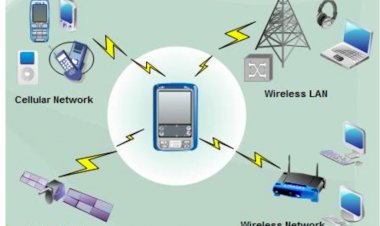
TCP/IP MODEL
The term TCP/IP model refers to Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. Protocols are rules that are to be followed and govern a certain communication network.

TCP/IP MODEL
The term TCP/IP model refers to Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. Protocols are rules that are to be followed and govern a certain communication network. This is the communication process which is broken down into small parts for it to be effective. The TCP/IP model is a summary of the OSI model. The TCP/IP model consists of four layers. The protocols show how data flows from the source to the destination.
READ ALSO: Online Exam Android App with Admin Panel
The layers are as follows
a) Application layer
b) Transport layer
c) Internet layer
d) Network layer.
READ ALSO: Customer Relationship Management System
- Application layer.
This is the highest level layer of the OSI model. The application layer helps the end users to interact with software developed or applications in devices.
The application layer consists of protocol layers such as:
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP): It is mainly used to send files from one computer to another.
- Terminal Network (TELNET): It deals with issues concerning connection of a local computer to another one which is remotely located.
- Domain Name System (DNS): It deals with issuing of a unique address to a new host that is using internet services.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) : This protocol helps us to be able to access information through the internet. Once allowed to have access to the data, it appears either in form of audio, video or text.
READ ALSO: Task Reminder app with Free Sourcecode
- Transport layer.
This layer deals with the transport of data between the source and the destination and ensures that the process of flow of data or information reaches its destination free from error. This layer also grants permission to services requesting transmission of data from a certain source to destination.
This layer consists of two protocols which are: a) Transmission Control Protocol which provides transport services for data and ensures that errors which may occur during transmission are rectified.
b) User Datagram Protocol.( UDP)
This protocol mainly specifies the port address of the destination and the port address of the source. UDP specifies that an error has occurred during transmission but does not specify the type of error that has occurred.
- Internet layer.
This layer deals with sending of packets of data through a network to its destination. The data is packed into packets known as IP Datagrams which have information of the source address and that of the destination.
- Network access layer.
This is the last layer found in the TCP/IP model. It is the combination of physical layer and the data link layer which are separate layers in the OSI model. It shows how information is transferred from one device to another when both devices are connected to the same network. Protocols found in this layer are Ethernet and token rings among others.
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR YOUTUBE CHANNEL BELOW TO WATCH MORE VIDEOS